Methods
Everything we have learned so far converges on this point... methods. The methods are the instruction/endpoints
of our smart contract, the client and other smart contracts will be calling or extending these methods.
You can define any number of methods required for your use case.
If you are new to the CIDL, we recommend you start learning from understanding what the CIDL
Definition
methods is an array of objects where each object is a method
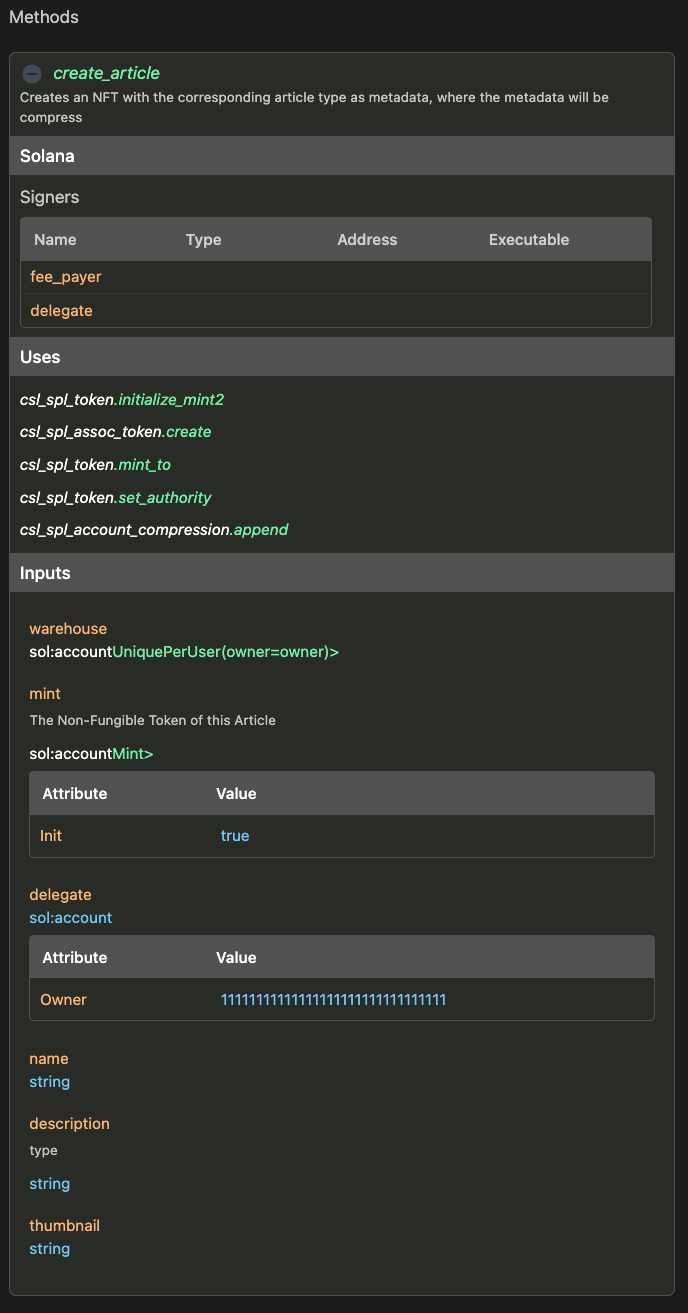
methods:
- name: create_article
summary: Creates an NFT with the corresponding article type as metadata, where the metadata will be compress
solana:
compress:
- type: Article
mode: append
signers:
- name: fee_payer
type: sol:account
attributes: [ sol:writable ]
- input: delegate
uses:
- csl_spl_token.initialize_mint2
- csl_spl_assoc_token.create
- csl_spl_token.mint_to
- csl_spl_token.set_authority
inputs:
- name: warehouse
type: sol:account<Warehouse, seeds.UniquePerUser(owner=owner)>
- name: mint
type: sol:account<csl_spl_token.Mint>
attributes: [ sol:init ]
description: The Non-Fungible Token of this Article
- name: delegate
type: sol:account
attributes: [ sol:owner=11111111111111111111111111111111 ]
- name: name
type: string
- name: description
type: string
- name: thumbnail
type: string
Check the Inventory guide to learn how to implement methods like the above
| Keyword | Type | Optionality | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| methods | Array<MethodBody> | Required |
Method Body
| Keyword | Type | Optionality | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Required | The name of the method, it must follow the targeted programming naming convention |
| summary | string | Recommended | Documentation summary of the method. Supports markdown |
| solana | Solana | Optional | |
| signers | Array<SignerBody> | Optional | |
| inputs | Array<InputBody> | Optional | |
| uses | Array<string> | Optional | List of reference methods in the form of ref.method_name, where ref is the value set in the imports |
Solana Method Extension
| Keyword | Type | Optionality | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| default-payer | boolean | Optional | By default, it is set to true. Set to false with an empty signer list to remove all signers from the method |
| compress | Array<CompressBody> | Optional | List of types to be compress. |
Compress Body
| Keyword | Type | Optionality | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | Type | ref.Type | Required | Can reference imported CIDLs in the form of ref.type_name, where ref is the value set in the imports |
| mode | append | insert_or_append | replace_leaf | verify_leaf | Required | How should this type be compress. Each mode corresponds to a method of the state compression program |
Signer Body
| Keyword | Type | Optionality | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Mutually exclusive | The name for the signing account. |
| type | Type | ref.Type | Mutually exclusive | Can reference imported CIDLs in the form of ref.type_name, where ref is the value set in the imports |
| input | string | Mutually exclusive | Reference to an input's name. It will set the input as a signer |
| attributes | Array<string> | Optional | Attributes to modify/extend the type. Only applicable when type is defined |
name/type are mutually exclusive with input. This means
that name/type needs to be set or input, both cannot be defined
at the same time.
Defined signers or inputs marked as signers will generate the following security check.
methods:
- name: method_with_custom_signer
signers:
- name: fee_payer
type: sol:account
attributes: [ sol:writable ]
- input: delegate
inputs:
- name: delegate
type: sol:account
attributes: [ sol:owner=11111111111111111111111111111111 ]
- Solana Native
- Solana Anchor
pub fn process_method_with_custom_signer(/* ... */) -> ProgramResult {
// ...
if fee_payer_info.is_signer != true {
return Err(CounterError::InvalidSignerPermission.into());
}
if delegate_info.is_signer != true {
return Err(CounterError::InvalidSignerPermission.into());
}
// ...
}
#[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct MethodWithCustomSigner<'info> {
#[account(
mut,
)]
pub fee_payer: Signer<'info>,
#[account(
owner=Pubkey::from_str("11111111111111111111111111111111").unwrap(),
)]
pub delegate: Signer<'info>,
}
Input Body
| Keyword | Type | Optionality | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Required | The name of the parameter, it must follow the targeted programming naming convention |
| type | native | extended | Type | ref.Type | Required | The data type of this parameter<br /><br />Can reference imported CIDLs in the form of ref.type_name, where ref is the value set in the imports |
| description | string | Recommended | Documentation of the input. Supports markdown |
| attributes | Array<string> | Optional | Attributes to modify/extend the type |
We can specify any native, extended, or custom data type to the input type.
Web-based documentation
The methods object can be visualized in the CIDL web-based doc. The documentation is automatically generated from our
vscode-codigo extension.
[//] # (This CIDL web-based doc can be generated by typing the command:)
[//] # (```shell)
[//] # (codigo solana generate ./counter.cidl --doc)
[//] # (```)
Next steps
Congratulations! 🎉👏 at this point, you should have a basic understanding of the CIDL, how to work with native, extended, and custom-defined types, and import other CIDL and implement methods. The next step on your journey is to start implementing use cases. You can follow our guides to start implementing use cases step by step or check our examples here
Join the Código community 💚
Código is a growing community of developers. Join us on Discord and GitHub